Financial planning is an unquestionable requirement for professional athletes, who are renowned for Contest Performance and burning through their six-, seven-, and, surprisingly, eight-figure pay rates. Numerous pro competitors earn in a single year or a couple of years what the normal laborer may not find in a lifetime, however, this can give a false sense of security.
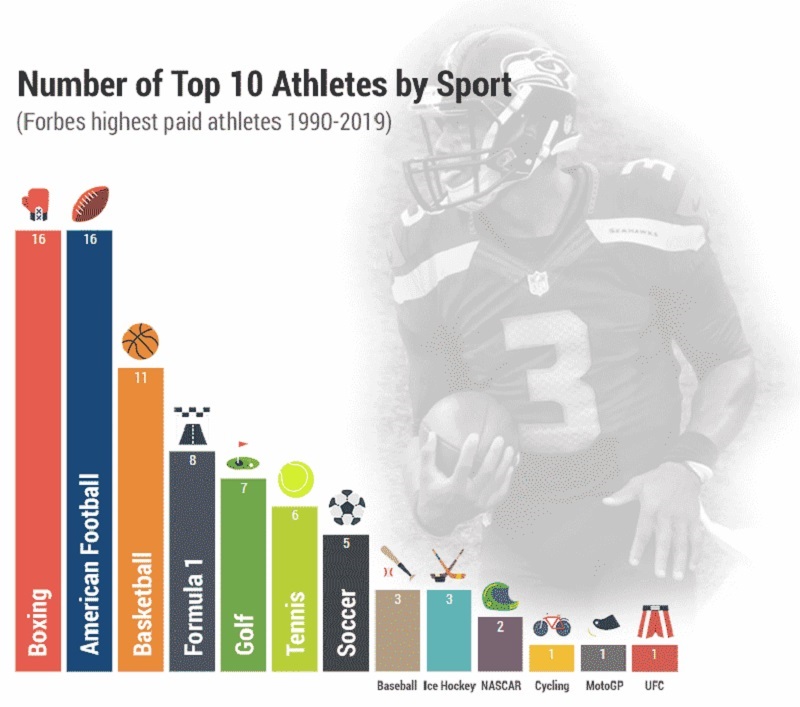
In recent years, the greatest agreements in NBA and NFL history have been agreed upon. For the 2019-2020 season, 28 NBA players received contracts that exceed $27.5M for the year, including Stephen Curry, the league’s highest earner, who gets more than $40M every year for their Previous Awards. In the NFL, the Kansas City Chiefs signed a 10-year $503M contract expansion with their quarterback, Patrick Mahomes. However, he’s in good company; in 2020-2021, numerous other NFL players also marked agreements for yearly Income Composition compensations going from $20-$43 million! These are the very most recent illustration of how, in the current century, proficient competitors’ salaries have detonated to phenomenal levels, igniting a discussion on whether they deserve them.
Professional competitors mess up the same way that others regularly do-helping battling loved ones; purchasing too many toys, garments, and eatery suppers; buying a greater number of houses than they need; and not putting something aside for what’s to come. An intensifying variable is that athletes will quite often be young when they suddenly find themselves with plenty of money.
Thus, here are the top things you most likely don’t know how athletes are paid, their pay structure to their employers, and What Aspects of the Income of a Professional Athlete contrast with those of normal people.
Athletes do not Officially have to Play to get Waged
Contingent upon the terms and provisions in a player’s agreement, unexpected conditions that leave them sidelined, for example, a physical issue or a performance droop may not adversely influence their pursuit. A few games preclude teams from releasing injured players until they are cleared, and as long as the injury was supported during sport-related exercises, the group is committed to paying. Suspensions, notwithstanding, are given as disciplines while a player is suspended, their pay is as well.
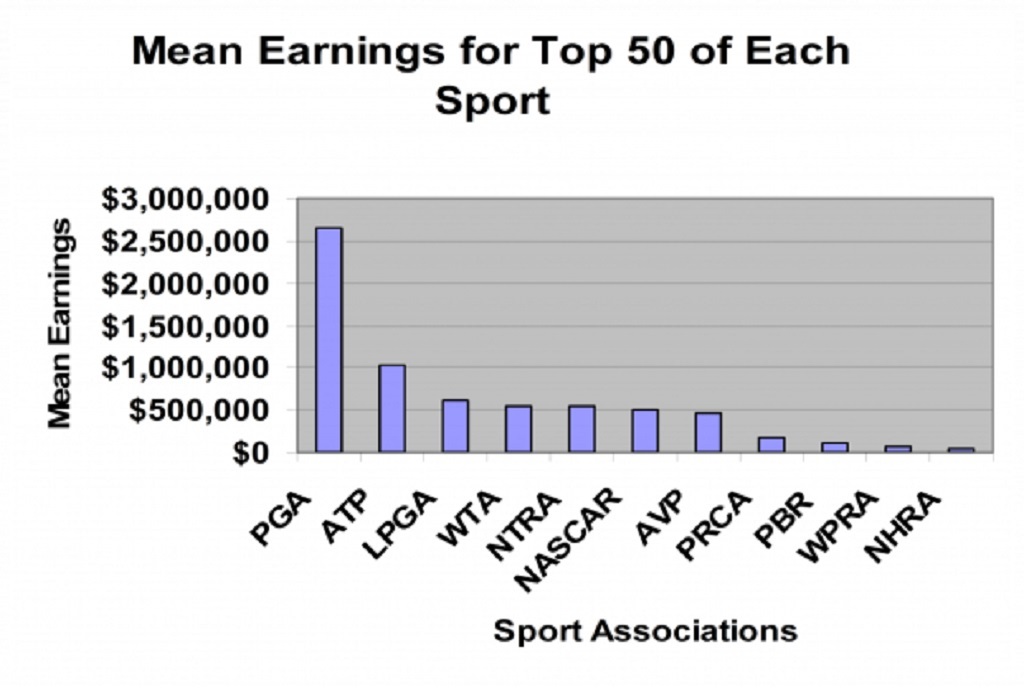
A Players’ Salary can differ Drastically from one Year to Another
In certain games, like proficient golf for instance, how much cash that players can earn every year is a bit more convoluted. Performance, tour status, and support all add to a player’s main concern, and that implies financial stability can be a worry from one year to another.
Numerous Players File for Bankruptcy After Retirement
Relatively speaking proficient football, basketball, and soccer players make a lot of cash yet that doesn’t continuously help them over the long haul. An expected one in each six pro football players files for bankruptcy within 12 years of resigning from the game due to lack of arranging, unsustainable lifestyles, and different variables.
Teams have found ways of Getting Around Salary Caps
Salary caps in sports are dollar amounts that teams are not permitted to surpass while paying their players. It holds the most affluent teams back from arranging the deck by spending more cash on the best players, yet there are astute ways of evading those rules. In football, the money that teams can offer players falls into two classifications: base compensations and signing bonuses. All of a player’s base salary counts in with the salary cap for that year, however, the signing bonus applies to the existence of the agreement, and that implies that it is spread across several years.
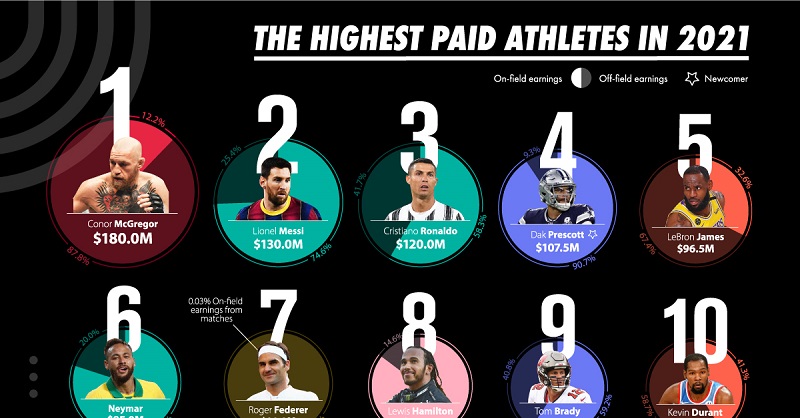
Pay Discrepancies between Teammates can Affect Performances
Studies have shown that baseball teams that have more players with equivalent salaries win more games. In basketball, teams with more compensation incongruities win more matches. Research has additionally shown that with regards to compensation, athletes value the idea of “fairness” over equality.
Tax Preparation for Athletes is substantially more Complicated
With large paychecks come big obligations … to Uncle Sam. Professional athletes at the highest levels in their games can make millions, and that implies that their assessment rates can approach 50%. What’s more, the individuals who travel to play are dependent upon extra tax assessment from each state they visit through what has become known as the “jock tax.”
The Gender Wage Gap is Worse in Professional Sports
In a rundown of the highest-paid athletes on the planet for 2015, the best 39 were men, and simply two women figured out how to break the top 100. Some contend that financial matters can clarify the orientation wage hole, with bigger crowds approaching more cash for men’s teams and their relationship, while others say that the mathematical still doesn’t make any sense. In professional basketball at the highest level, the base compensation for men is almost five times higher than the maximum salary for women.
Teams can Sue Ex-Players for Overpayment
On account of an administrative blunder, one football player got a big payday from his previous team, as much as $40,000. When the association understood that the mistake had been made, it sued the player and an appointed authority decided that he was answerable for repaying it. At the point when he didn’t pay, an assertion hearing brought about a settlement of around $21,000 to be reimbursed.

No responses yet